Atlassian REST API Search Endpoints Deprecation
As per Atlassian's changelog notification, the Jira Platform REST endpoints listed below will be deprecated and no longer available for use after August 1st 2025*. We recommend rewriting your code before this date, as the old endpoints will only continue to work until then.
*This date changed from May 1st to August 1st, but you can safely make any code rewrites straight away.
Deprecation Reports
ScriptRunner for Jira Cloud provides you with Deprecation Reports that highlight the usage of Atlassian's deprecated endpoints and fields in your instance.
Rewrite Your Scripts with HAPI: Examples
It's our recommendation that your rewrite deprecated endpoints using HAPI as this will simplify your scripts by significantly reducing script length, making them easier to read. HAPI scripts are also easier to maintain, reducing the time spent troubleshooting when scripts stop working.
GET /rest/api/2|3|latest/search
Recommended Alternative
GET /rest/api/{2|3|latest}/search/jql
For more information, refer to Atlassian's Jira Cloud platform REST API documentation.
Key Differences
| Differences | Notes |
|---|---|
Issue details | Only Issue IDs are returned by default. Use the fields property to request additional details. |
| Recent updates | The new |
| Pagination | Replaced startAt with nextPageToken for improved pagination. Random page access is no longer supported. |
| Response structure | The new endpoint returns SearchAndReconcileResults, which includes a nextPageToken and a slightly different issue format. |
| Removed parameters | validationQuery, startAt |
| Comments and Changelog | This function returns a maximum of 20 comments and 20 change log items. Use a separate request to fetch more. |
| JQL query limitations | Unbounded JQL queries, meaning queries with an empty JQL string, will result in a 400 Bad Request error message. |
| Response format | The new endpoint returns a more concise response by default unless customised with additional request parameters such as fields and expand. |
Use HAPI for Simplified Issue Search
HAPI’s Issue Search provides a simpler way to retrieve all issues that match your query.
groovydef issueKeys = Issues.search("project = TEST AND issueType = Bug") return issueKeys.collect { issue -> issue.key }
POST /rest/api/2|3|latest/search
Recommended Alternative
POST /rest/api/{2|3|latest}/search/jql
For more information, refer to Atlassian's Jira Cloud platform REST API documentation.
Key Differences
| Differences | Notes |
|---|---|
Issue details | Only Issue IDs are returned by default. Use the fields property to request additional details. |
| Recent updates | The new reconcileIssues parameter ensures that recently updated or created issues are included in search results. This keeps search results up to date by automatically incorporating recently modified issues, even if they were not originally part of the search criteria. This is especially useful for instantly reflecting the latest changes. |
| Pagination | Replaced startAt with nextPageToken for improved pagination. Random page access is no longer supported. |
| Response structure | The new endpoint returns SearchAndReconcileResults, which includes a nextPageToken and a slightly different issue format. |
| Removed parameters | validationQuery, startAt |
| Comments and Changelog | This function returns a maximum of 20 comments and 20 change log items. Use a separate request to fetch more. |
| JQL query limitations | Unbounded JQL queries, meaning queries with an empty JQL string, will result in a 400 Bad Request error message. |
| Response format | The new endpoint returns a more concise response by default unless customised with additional request parameters such as fields and expand. |
HAPI’s Issue Search provides a simpler way to retrieve all issues that match your query. This eliminates the need to manage pagination or process API responses manually, as HAPI automatically fetches all matching issues, resulting in cleaner and more efficient code.
groovydef issueKeys = Issues.search("project = TEST AND issueType = Bug") return issueKeys.collect { issue -> issue.key }
POST /rest/api/2|3|latest/search/id
Recommended Alternative
POST /rest/api/{2|3|latest}/search/jql
For more information, refer to Atlassian's Jira Cloud platform REST API documentation.
Key Differences
| Differences | Notes |
|---|---|
| Full issue details | Unlike the old API, the new API returns complete issue details, not just issue IDs. |
| Reconciliation for consistency | The new reconcileIssues parameter ensures that recent updates or newly created issues are included in the search results. |
| New parameters |
|
| Pagination support | The new API includes pagination support, allowing you to fetch large result sets in multiple requests. |
You can easily achieve the functionality by using HAPI. This framework abstracts away the pagination and makes it simpler to work with JQL queries.
Example code with HAPI:
groovyIssues.search("project = TEST AND issueType = Bug").collect{it.id}
Rewrite Your Scripts with Unirest: Examples
It's our recommendation that your rewrite deprecated endpoints using HAPI as this will simplify your scripts by significantly reducing script length, making them easier to read. HAPI scripts are also easier to maintain, reducing the time spent troubleshooting when scripts stop working.
If you prefer to rewrite your scripts utilising HAPI at a later date, you can use the guidance provided in this section to modify Unirest requests.
GET /rest/api/2|3|latest/search
Rewrite Guidance
If you are not using HAPI, you must update your implementation using a different method. In most cases, the response processing from the old endpoint can be retained with modifications to request parameters when adopting the new API. Some exclusions apply specifically in handling pagination.
Without Pagination
groovyfinal jqlQuery = "project = TEST AND issueType = Bug" def searchReq = get("/rest/api/2/search/jql") .queryString("jql", jqlQuery) .queryString("maxResults", 100) // Adjust as needed, default is usually 50 .queryString("fields", "key, status, assignee") // Specify required fields .queryString("expand", "names, schema") // Optional expansions .asObject(Map) assert searchReq.status == 200 def searchResult = searchReq.body as Map // If the user would like to return or print the issue key (searchReq.body.issues as List<Map>)?.each { logger.info("The issue key is ${it.key}") } return searchResult
Handling Pagination
When querying using the new Jira search API, the response may include a nextPageToken, indicating that more results are available. To fetch the next page, include this token in a subsequent request instead of the standard JQL parameter. Below is an example of how to handle this in Groovy using a loop to fetch all pages:
groovydef results = [] def nextPageToken = null final jqlQuery = "project = TEST AND issueType = Bug" do { def request = get("/rest/api/2/search/jql") .queryString("jql", jqlQuery) .queryString("maxResults", 1) // Adjust as needed, default is usually 50 .queryString("fields", "key, status, assignee") .queryString("expand", "names, schema") if (nextPageToken) { // Only adds nextPageToken if it's not null request.queryString("nextPageToken", nextPageToken) } def searchReq = request.asObject(Map) assert searchReq.status == 200 def searchResult = searchReq.body as Map results << searchResult nextPageToken = searchResult.nextPageToken // Gets nextPageToken } while (nextPageToken) // Continues fetching until no more pages remain return results
This approach ensures that all issues matching the query are retrieved, handling pagination dynamically until no more pages remain.
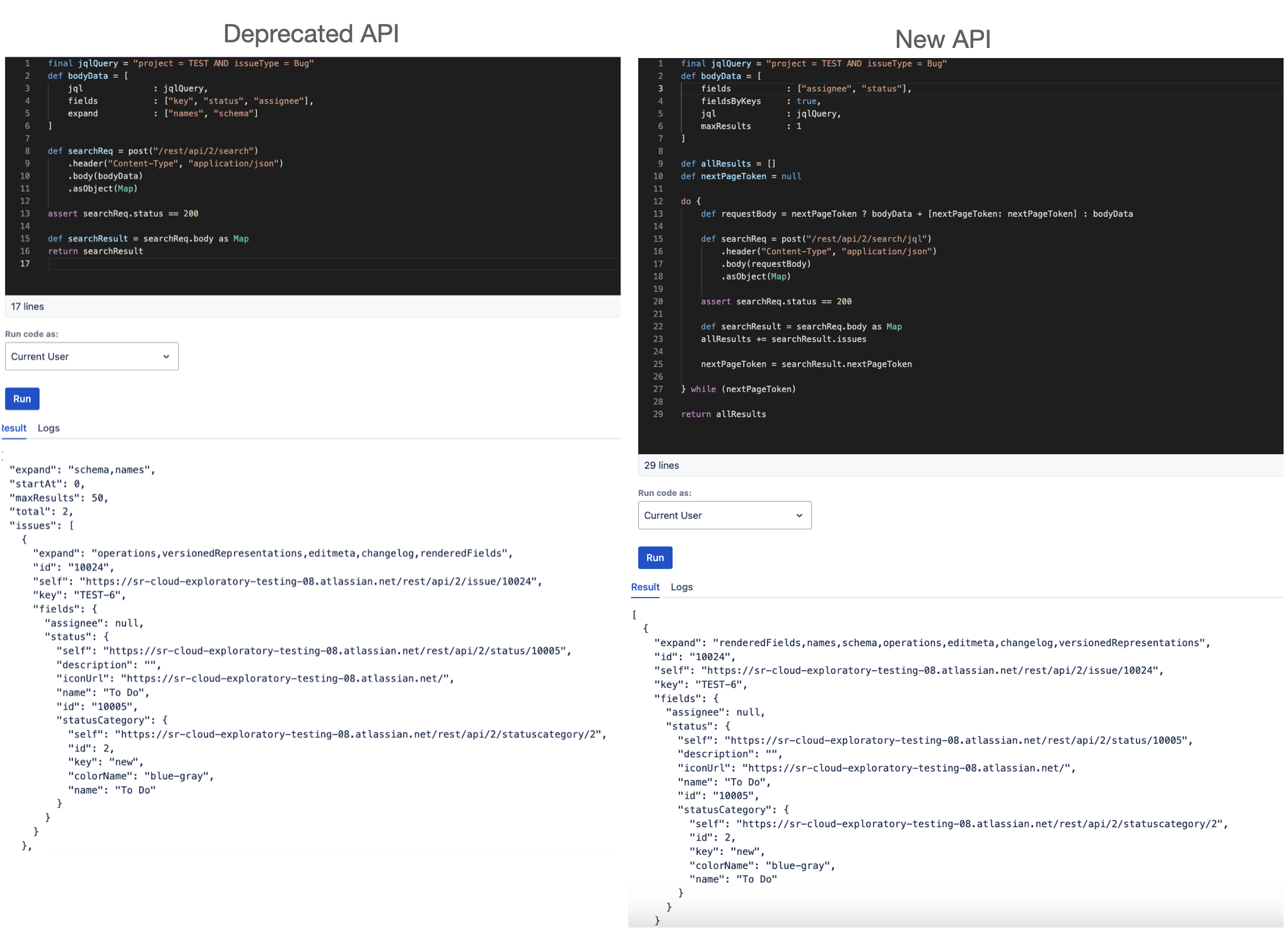
POST /rest/api/2|3|latest/search
Rewrite Guidance
Most of the existing response handling remains the same, but the request structure must be adjusted to align with the new API. Additionally, pagination should be handled using nextPageToken instead of startAt.
Without Pagination
To search for issues in Jira using a JQL query, you can use the following code:
groovyfinal jqlQuery = "project = TEST AND issueType = Bug" def bodyData = [ fields : ["assignee", "status"], fieldsByKeys : true, jql : jqlQuery, maxResults : 1 // Adjust as needed, default is usually 50 ] def searchReq = post("/rest/api/2/search/jql") .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body(bodyData) .asObject(Map) assert searchReq.status == 200 def searchResult = searchReq.body as Map return searchResult
Handling Pagination
If your search returns multiple pages of results, you can handle pagination automatically by checking for the nextPageToken and looping through all pages. Here’s how you can modify the code to retrieve all results:
groovyfinal jqlQuery = "project = TEST AND issueType = Bug" def bodyData = [ fields : ["key", "assignee", "summary", "description"], fieldsByKeys : true, jql : jqlQuery, maxResults : 100 // Adjust as needed, default is usually 50 ] def allResults = [] def nextPageToken = null do { def requestBody = nextPageToken ? bodyData + [nextPageToken: nextPageToken] : bodyData def searchReq = post("/rest/api/2/search/jql") .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body(requestBody) .asObject(Map) assert searchReq.status == 200 def searchResult = searchReq.body as Map allResults += searchResult.issues nextPageToken = searchResult.nextPageToken } while (nextPageToken) return allResults
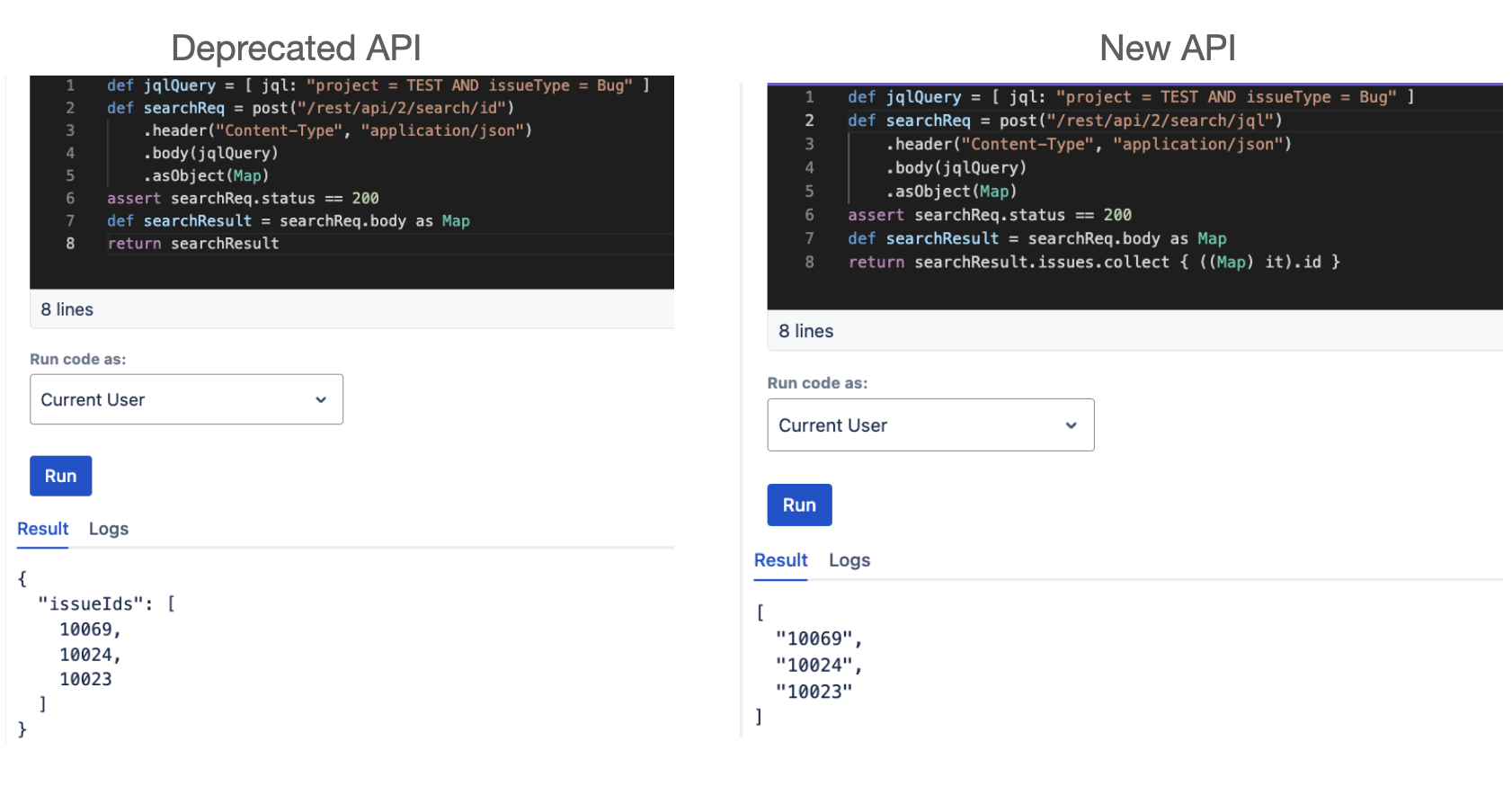
POST /rest/api/2|3|latest/search/id
If you are not using HAPI, you'll need to update your implementation. For 50 or fewer results, the query can be handled without pagination. Otherwise, pagination management is required.
Rewrite Guidance
The transition to the new endpoint requires modifying request parameters while keeping the response processing similar. The new API returns full issue details instead of just IDs, so filtering out only the IDs may be necessary. Handling pagination requires adapting to the nextPageToken mechanism.
Without Pagination
groovyfinal jqlQuery = [ jql: "project = TEST AND issueType = Bug" ] def searchReq = post("/rest/api/2/search/jql") .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body(jqlQuery) .asObject(Map) assert searchReq.status == 200 def searchResult = searchReq.body as Map return searchResult.issues.collect { ((Map) it).id }
Handling Pagination
The endpoint returns a nextPageToken in the response, which indicates that additional results are available. You'll need to handle pagination by looping through the pages until all issues are retrieved.
Example implementation with Pagination Support
groovydef issueIds = [] def nextPageToken = null final jqlQuery = [ jql: "project = TEST AND issueType = Bug" ] do { def requestBody = nextPageToken ? [ nextPageToken: nextPageToken ] : jqlQuery def searchReq = post("/rest/api/2/search/jql") .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body(requestBody) .asObject(Map) assert searchReq.status == 200 def searchResult = searchReq.body as Map issueIds += searchResult.issues.collect { ((Map) it).id } nextPageToken = searchResult.nextPageToken } while (nextPageToken) return issueIds
POST /rest/api/2|3|latest/expression/eval
Recommended Alternative
Evaluate Jira expression using enhanced search API:
POST /rest/api/3/expression/evaluate
For more information, refer to Atlassian's Jira Cloud platform REST API documentation.
Key Differences
| Differences | Notes |
|---|---|
| Bounded JQL queries | The API (/evaluate) requires setting maxResults (up to 5000). Unbounded queries will return a 400 Bad Request error message. |
| Response structure | The API returns JExpEvaluateJiraExpressionResultBean instead of JiraExpressionResultBean. |
| JQL validation | The API doesn’t validate JQL queries automatically. Invalid queries will result in errors that must be handled manually. |
| Pagination changes |
|
Rewrite Guidance
Most of the response processing can be maintained with adjustments to request parameters. The key differences include handling bounded JQL queries (setting maxResults) and switching pagination to nextPageToken. Additionally, JQL queries are no longer validated automatically and errors need manual handling.
Without Pagination
Groovy script example that demonstrates how to evaluate a Jira expression using this new API.
groovydef bodyData = '''{ "context": { "issue": { "key": "TEST-9" }, "issues": { "jql": { "query": "project = TEST", "maxResults": 1 } }, "project": { "key": "TEST" } }, "expression": "{ key: issue.key }" }''' def evalReq = post("/rest/api/3/expression/evaluate") .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body(bodyData) .asObject(Map) assert evalReq.status == 200 def evalResult = evalReq.body as Map return evalResult
Handling Pagination
To handle pagination with nextPageToken, modify the code to keep fetching results until there are no more pages. Example:
groovydef allResults = [] def nextPageToken = null do { def bodyData = '''{ "context": { "issue": { "key": "TEST-9" }, "issues": { "jql": { "query": "project = TEST", "maxResults": 1 } }, "project": { "key": "TEST" } }, "expression": "{ key: issue.key }" }''' if (nextPageToken) { bodyData = bodyData.replace('"maxResults": 1', '"maxResults": 1, "nextPageToken": "' + nextPageToken + '"') } def evalReq = post("/rest/api/3/expression/evaluate") .header("Content-Type", "application/json") .body(bodyData) .asObject(Map) assert evalReq.status == 200 def evalResult = evalReq.body as Map allResults.addAll(evalResult.value) nextPageToken = evalResult.meta?.issues?.jql?.nextPageToken } while (nextPageToken) return allResults