Work with Entity Properties
With HAPI, you can easily set and retrieve entity properties.
Entity properties are key-value pairs that can be stored against Jira entities, such as Projects, Issues, Users and Comments. They can tag information to such entities, and they can be stored, read or deleted programmatically. You can refer to Atlassian's Jira Cloud platform documentation to find out more.
The key of an entity property is always a string. The value can be a string, an integer, a long, a Boolean, or a JSON. We've provided some examples below that demonstrate how the value of an entity property can be a String, a boolean, a simple JSON, a number (long or integer), or a JSONArray.
groovy{ "key": "testProperty", "value": "the value of the property" }
groovy{ "key": "testProperty", "value": true }
groovy{ "key": "testProperty", "value": { "firstEntry": "one", "secondEntry": "two" } }
groovy{ "key": "testProperty", "value": 5 }
groovy{ "key": "testProperty", "value": [ { "propertyOne": 1, "propertyTwo": 2 }, { "propertyA": "A", "propertyB": "B" } ] }
Set and retrieve entity properties
HAPI equips entities like Projects, Issues, Users and Comments with a Groovy object called EntityProperties. This provides methods to set and retrieve properties stored against the specific entity that made the object available.
To use the EntityProperties object:
- Choose the entity (project/user/issue/comment) whose properties you want to interact with.
- Extract the
EntityPropertiesobject. - Call the methods provided by the
EntityPropertiesobject to set or get properties.
Example use of EntityProperties
Here's an example of how to use EntityProperties for a project:
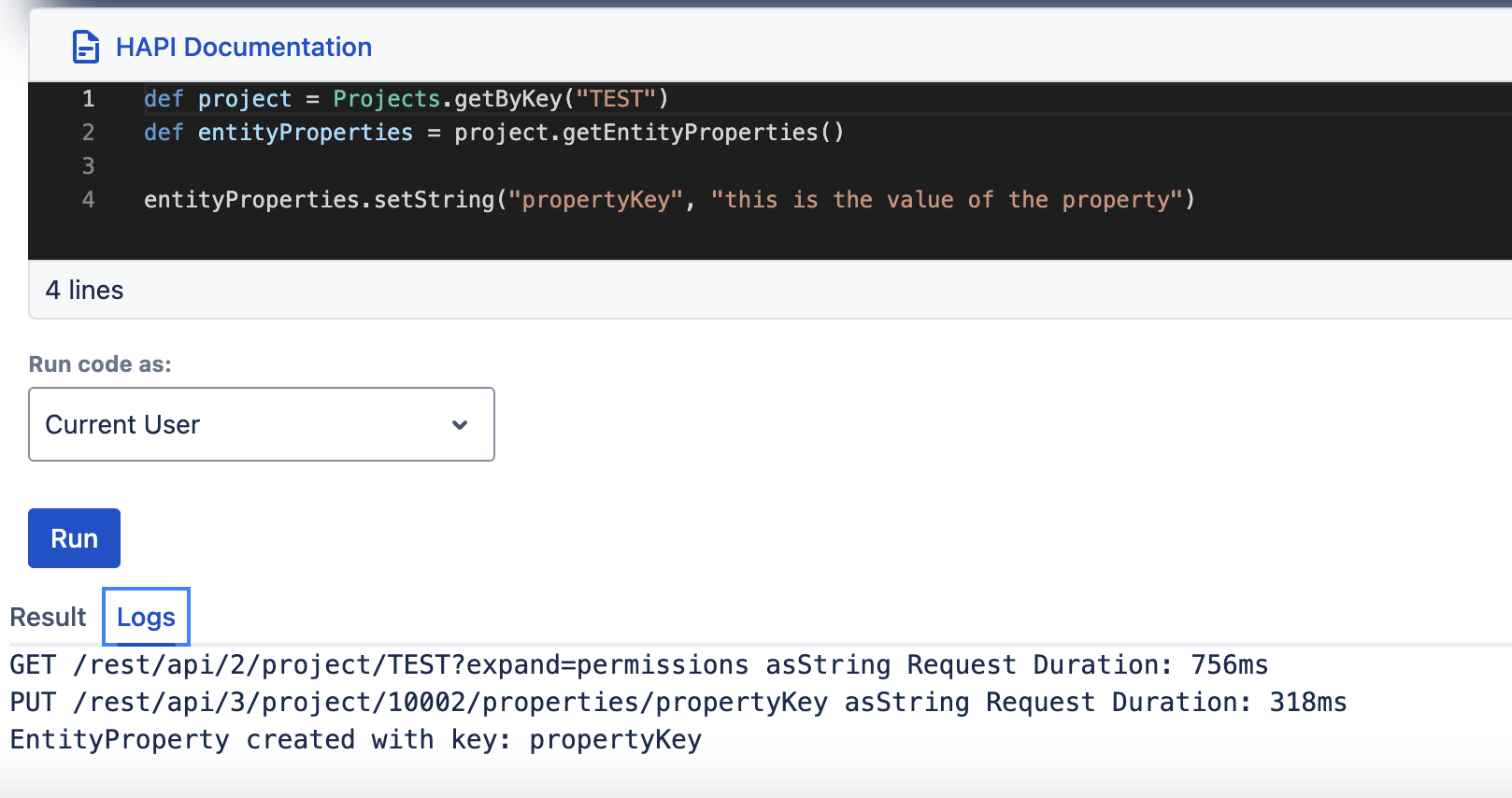
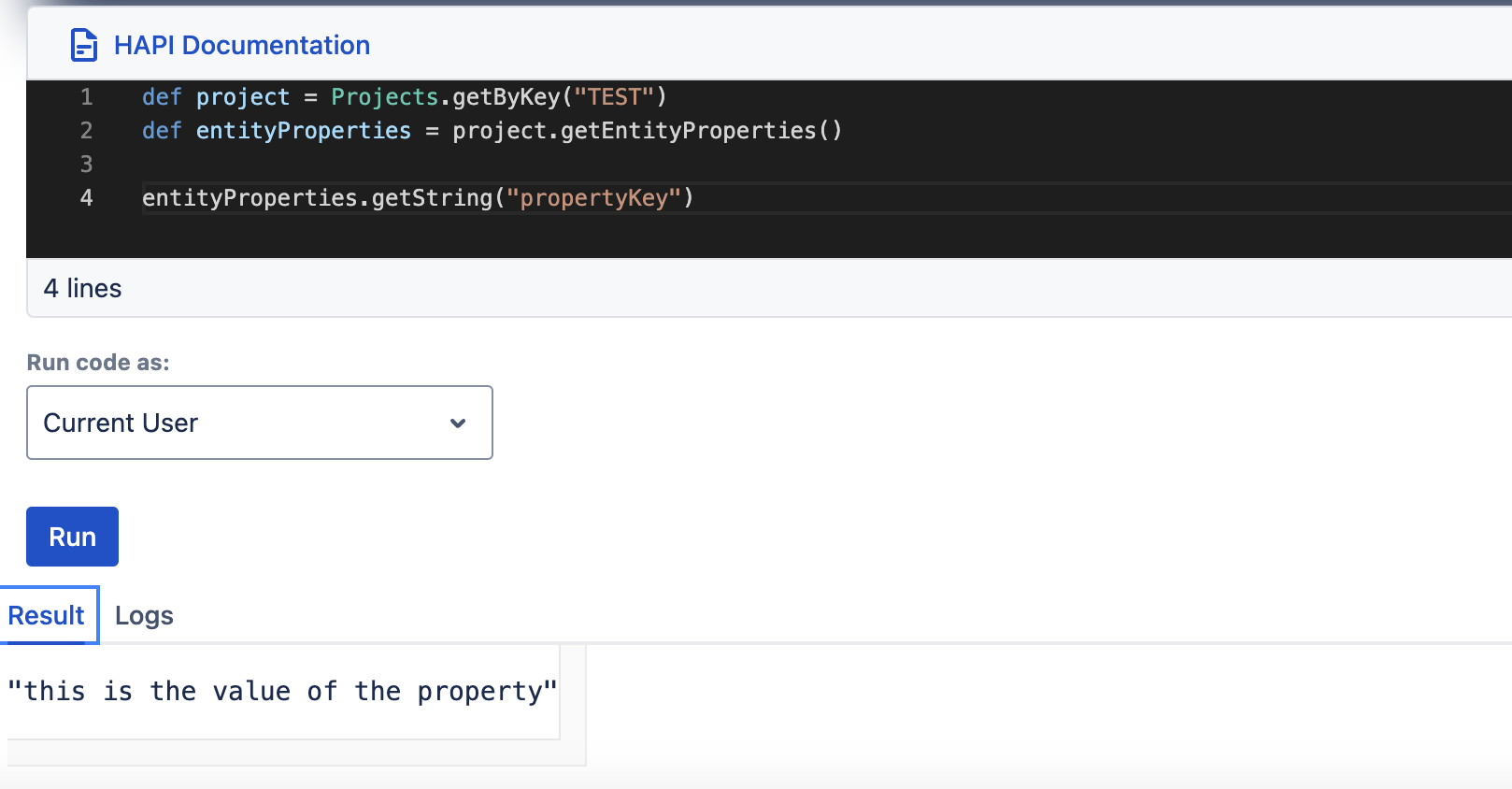
groovydef myProject = Projects.getByKey("TEST") // Obtain the entity def entityProperties = myProject.getEntityProperties() // Extract the EntityProperties object from the entity entityProperties.setString("testProperty", "the value of the property") // Call the methods provided by the EntityProperties object // to set or get properties entityProperties.getString("testProperty")
EntityProperties objects are entity-specific. When obtained from a certain entity (such as a project, user, issue, or comment), an EntityProperties object will interact only with the properties of that particular entity.
For example:
groovyProjects.getByKey("TST1").getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against Project TST1 Projects.getByKey("TST2").getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against Project TST2 Users.getByAccountId("aaaaa-11111").getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against User aaaaa-11111 Users.getByAccountId("bbbbb-22222").getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against User bbbbb-22222 Issues.getByKey("CCC-1").getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against Issue CCC-1 Issues.getByKey("CCC-2").getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against Issue CCC-2 List<Comment> comments = Issues.getByKey("CCC-1").getComments() Comment firstComment = comments.getAt(0) // assuming the list of comments is not empty firstComment.getEntityProperties() // will interact with properties stored against that comment
Methods of the EntityProperties object
The EntityProperties object provides various methods that allow you to interact with an entity's properties. Setters and getters will allow you to set and retrieve entity properties based on the specified property type.
Calling a setter method with the key of an existing property will overwrite with a new value. Calling a getter method with a specific return type should only be done if the property's type is known.
For example, if a property has been set using the setLocalDate method, the getLocalDate method can be expected to function correctly.
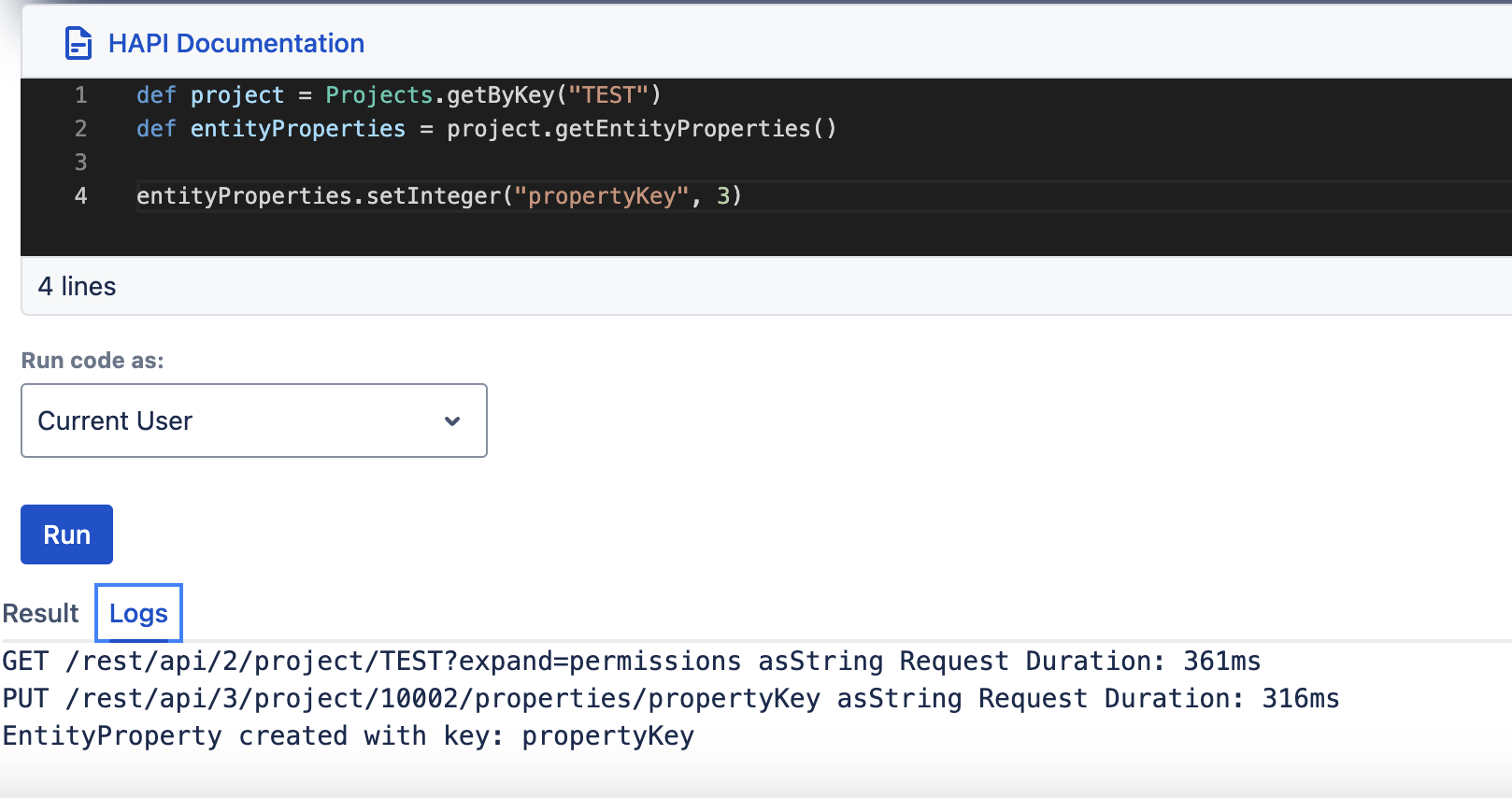
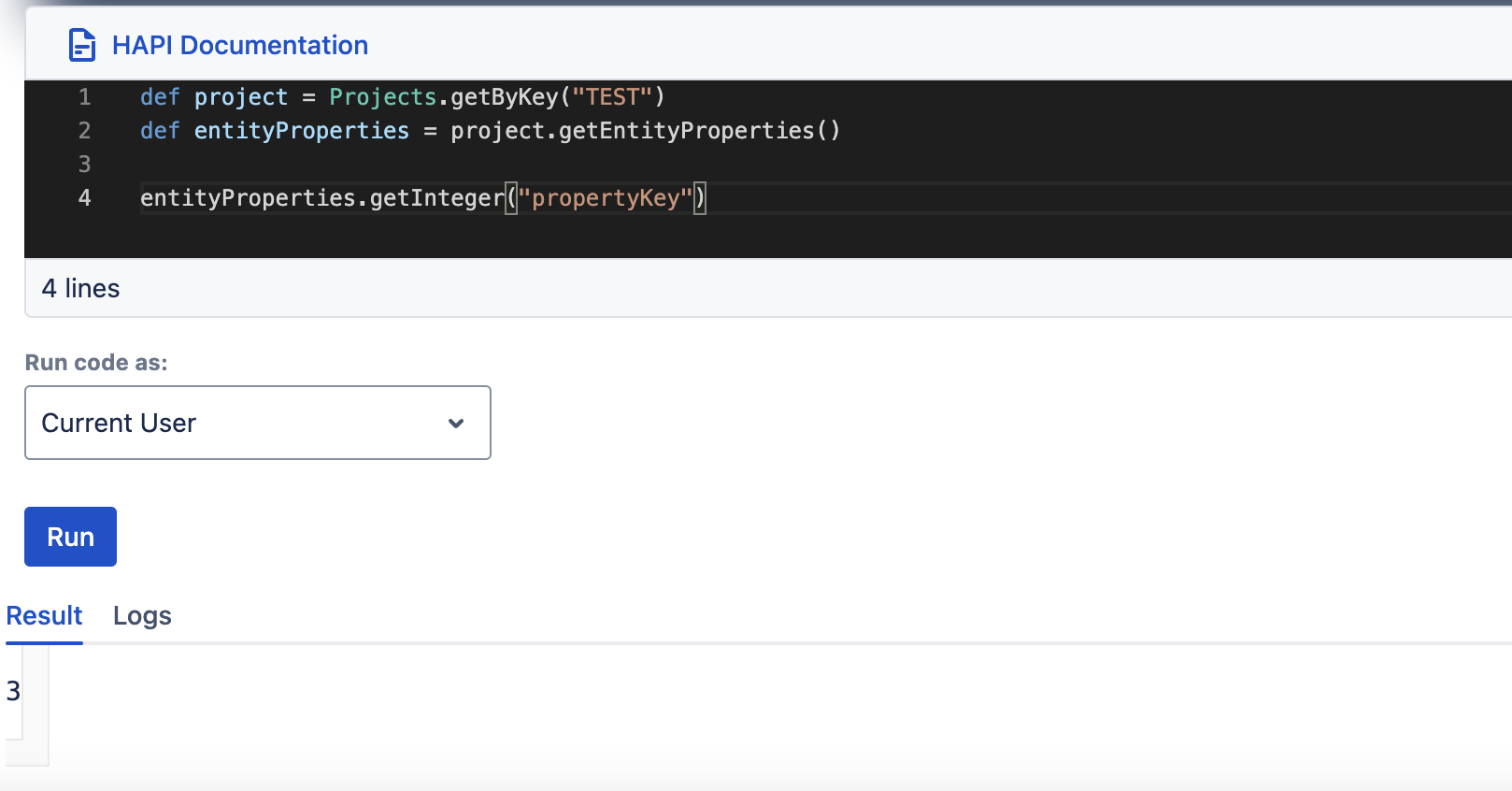
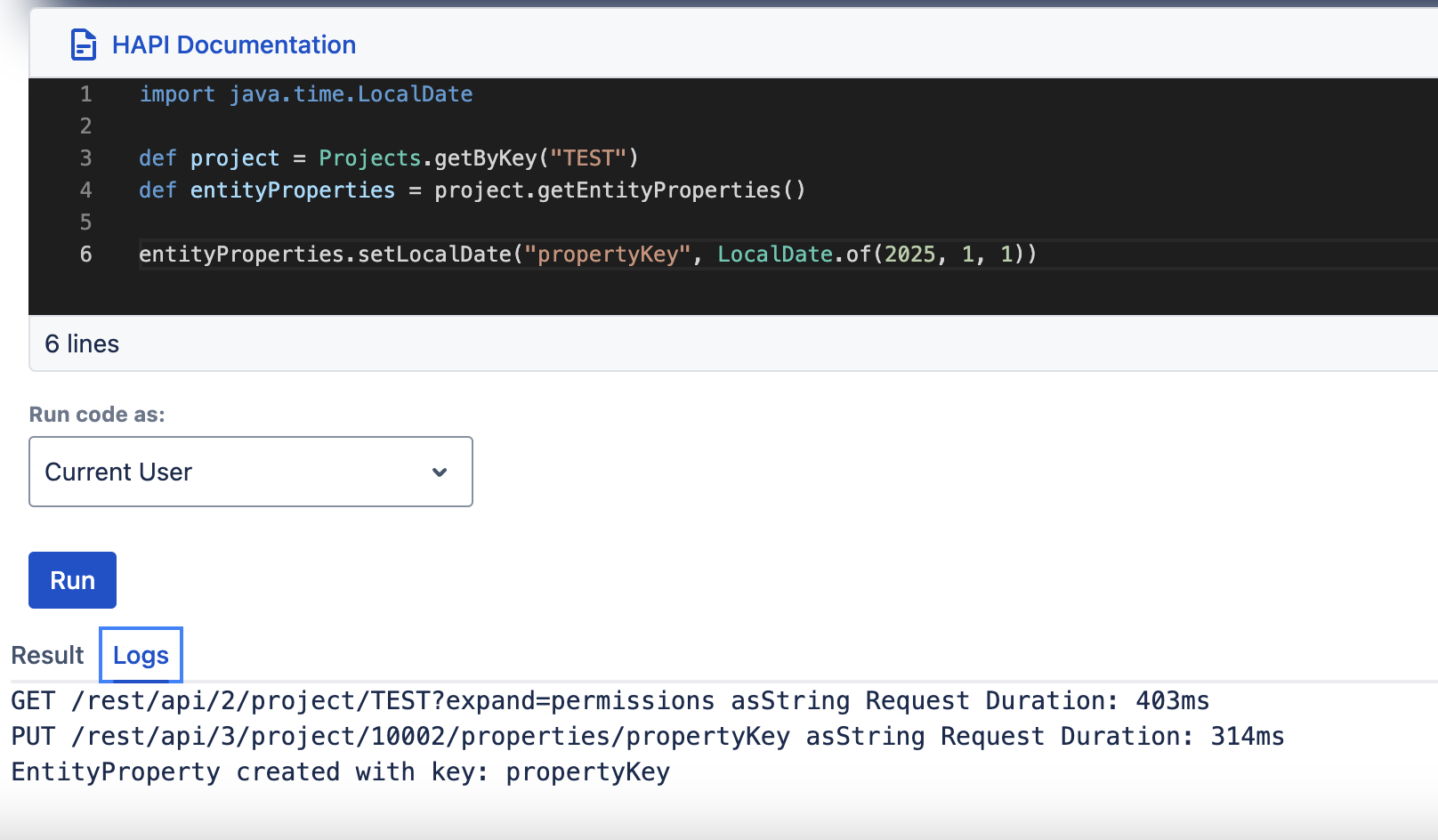
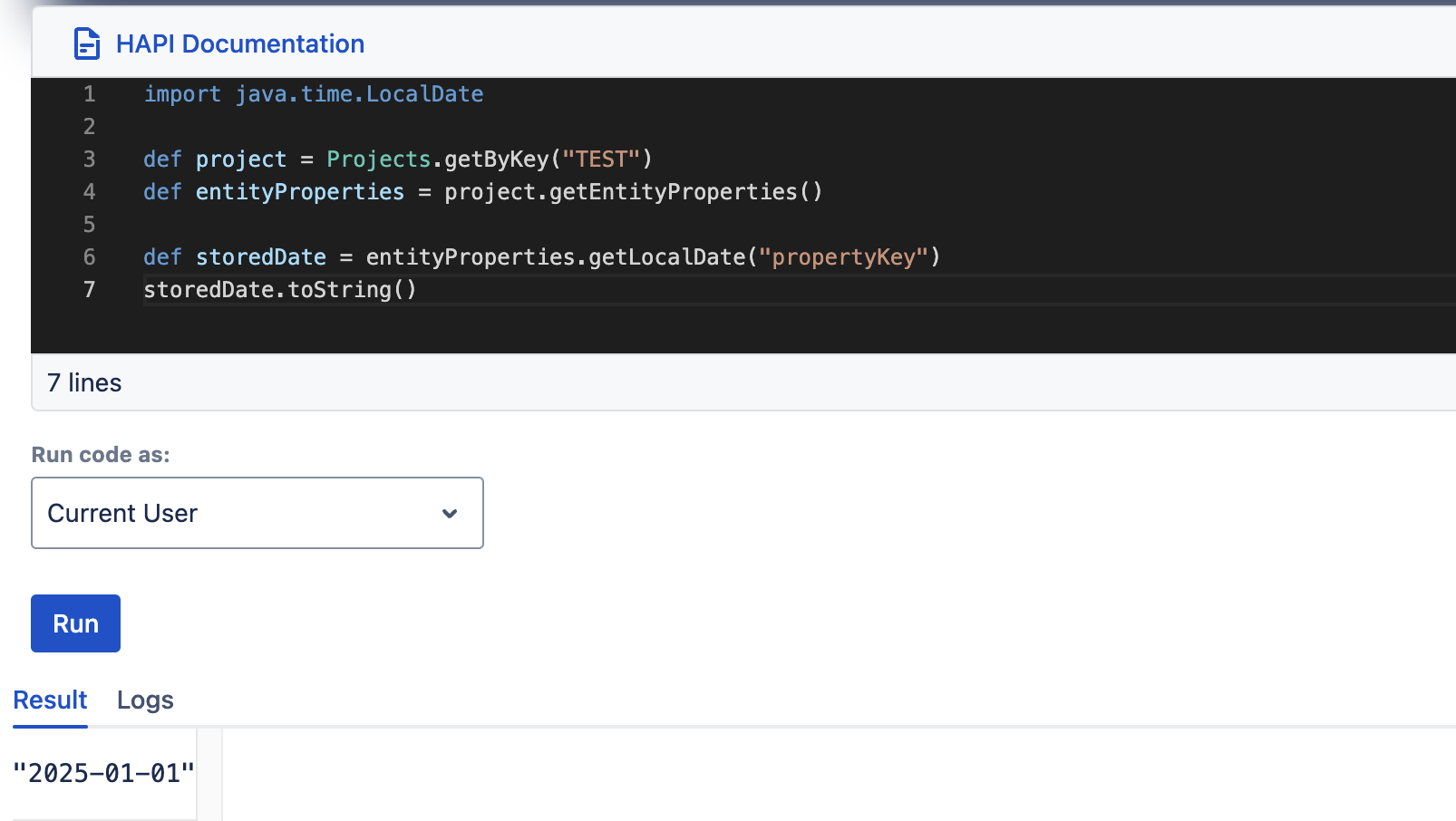
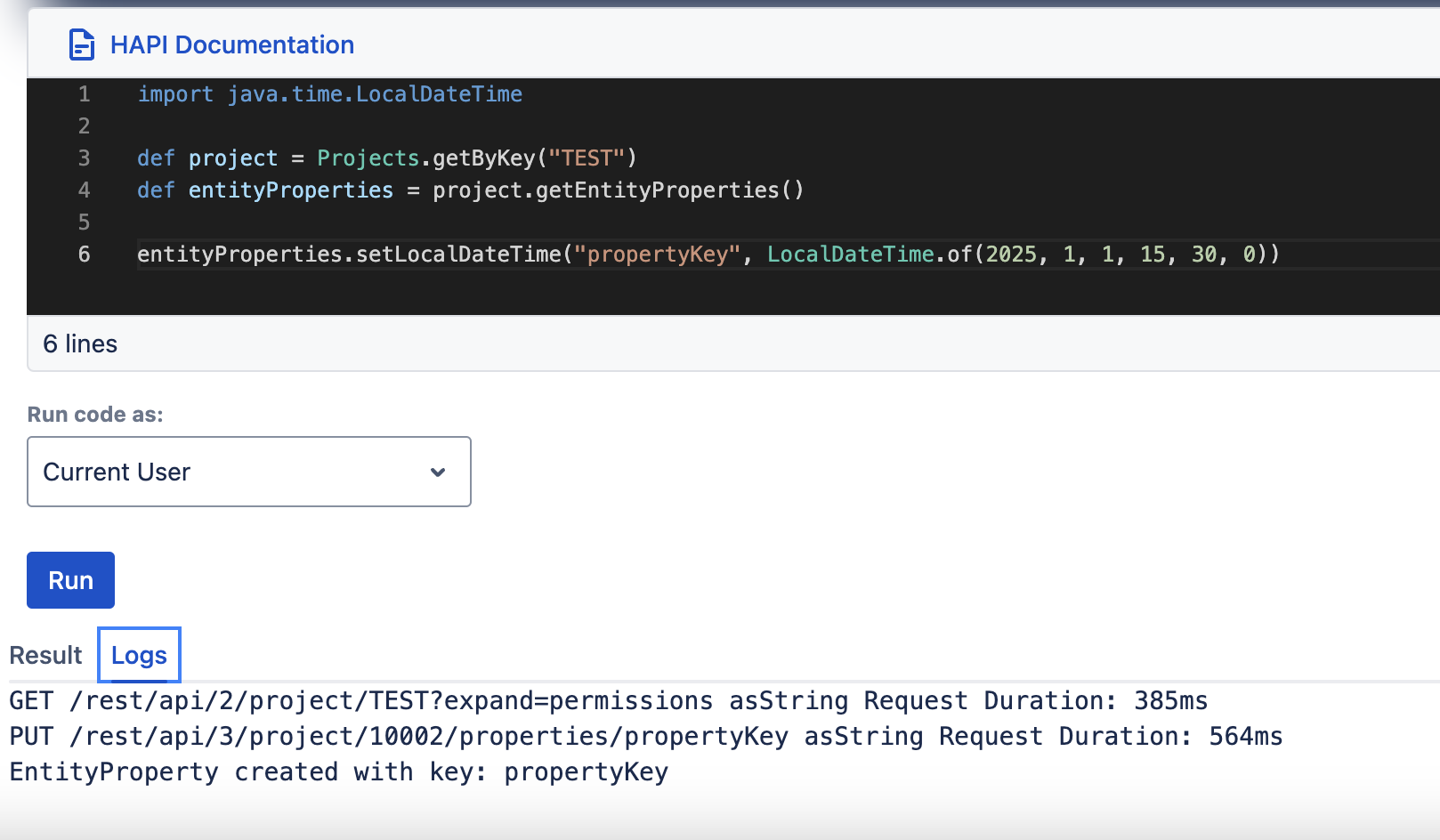
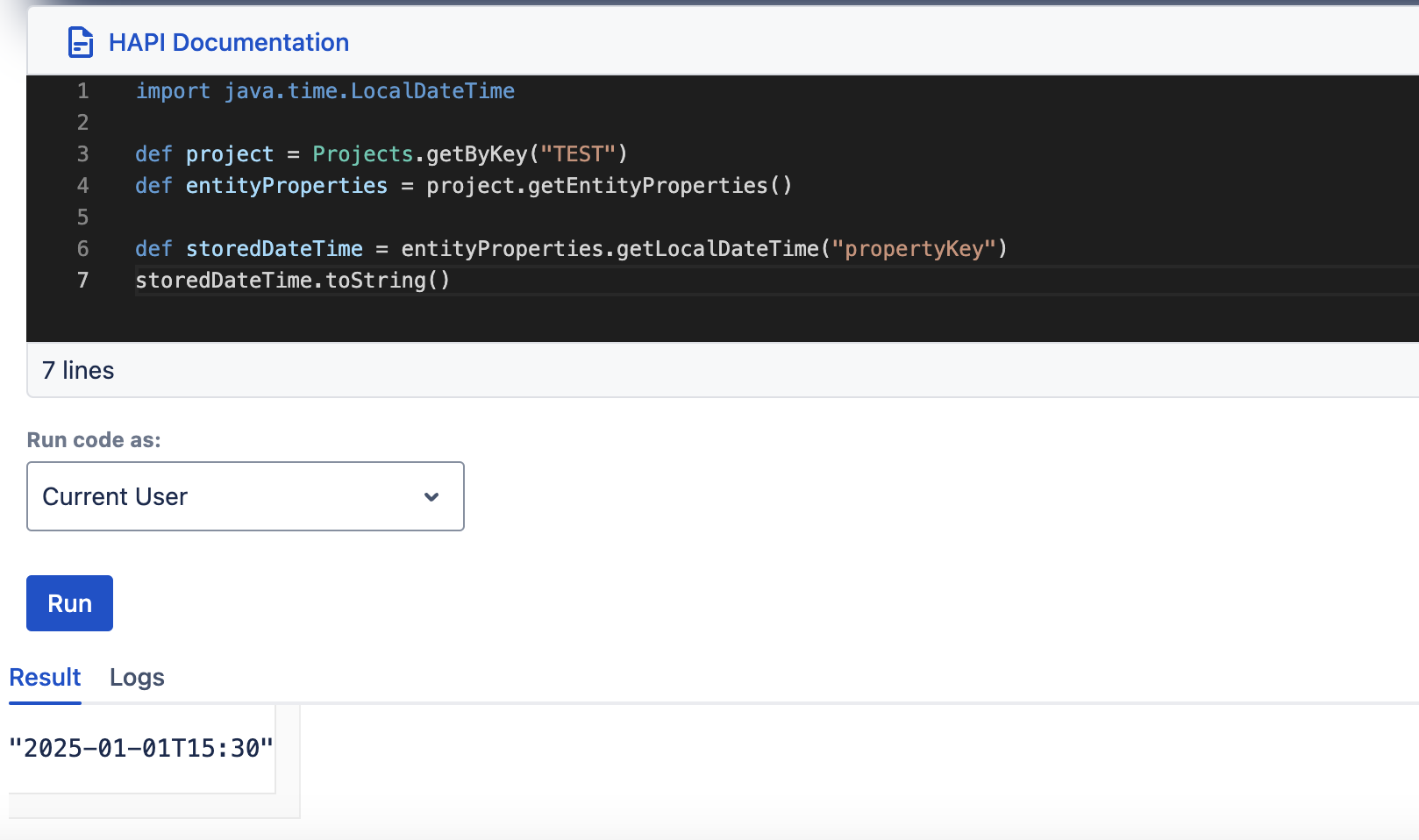
setString(String key, String value)getString(String key)setInteger(String key, Integer value)getInteger(String key)setLong(String key, Long along)getLong(String key)setBoolean(String key, Boolean bool)getBoolean(String key)setLocalDate(String key, LocalDate localDate)getLocalDate(String key)setLocalDateTime(String key, LocalDateTime localDateTime)getLocalDateTime(String key)
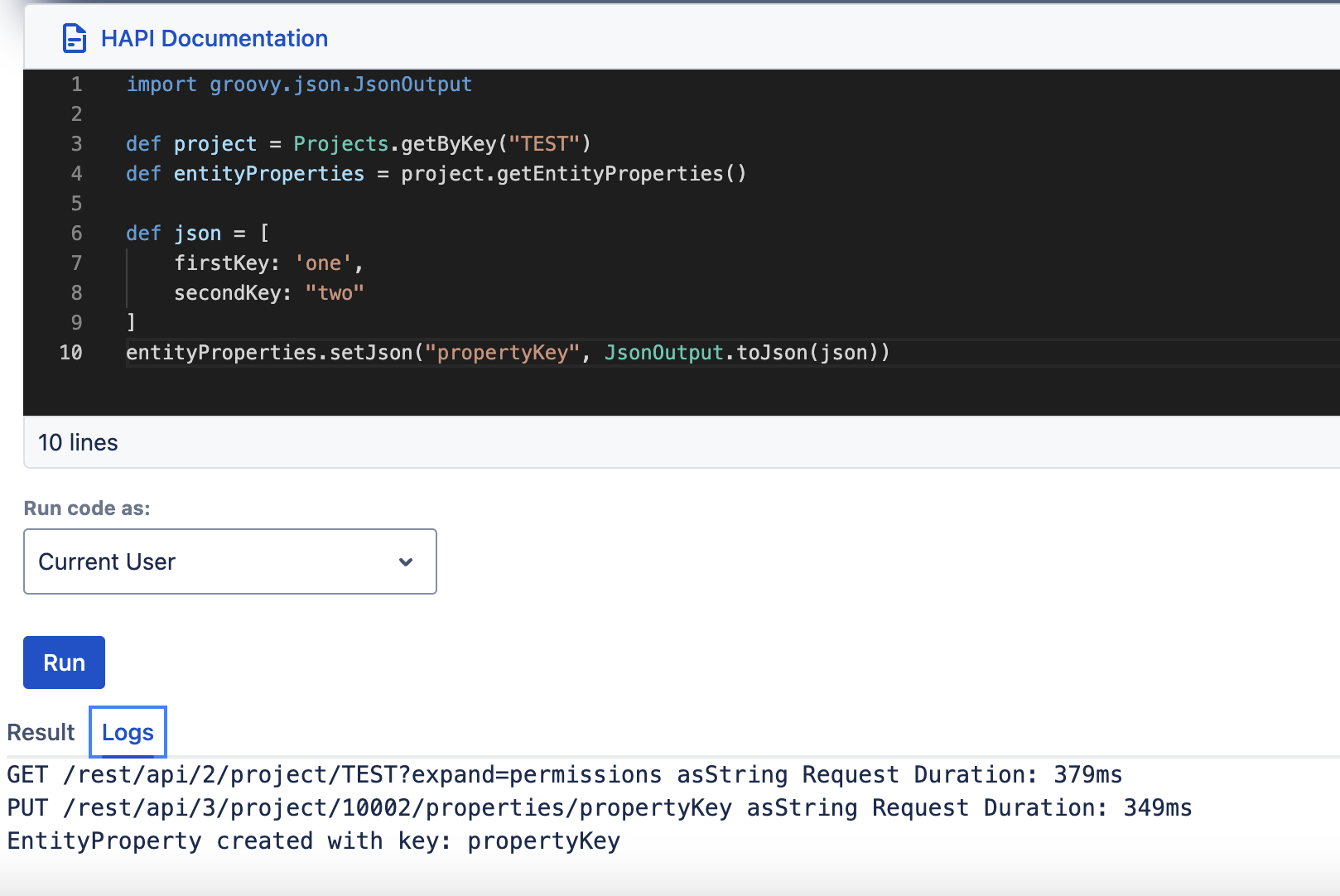
Whilst setting a JSON gives you options, it's important to note that the JSON string for the property value must be correctly formatted.
An object can be set as a property value as long as it is serializable to a JSON. The resulting JSON value can then be deserialized into the original class using a getter method.
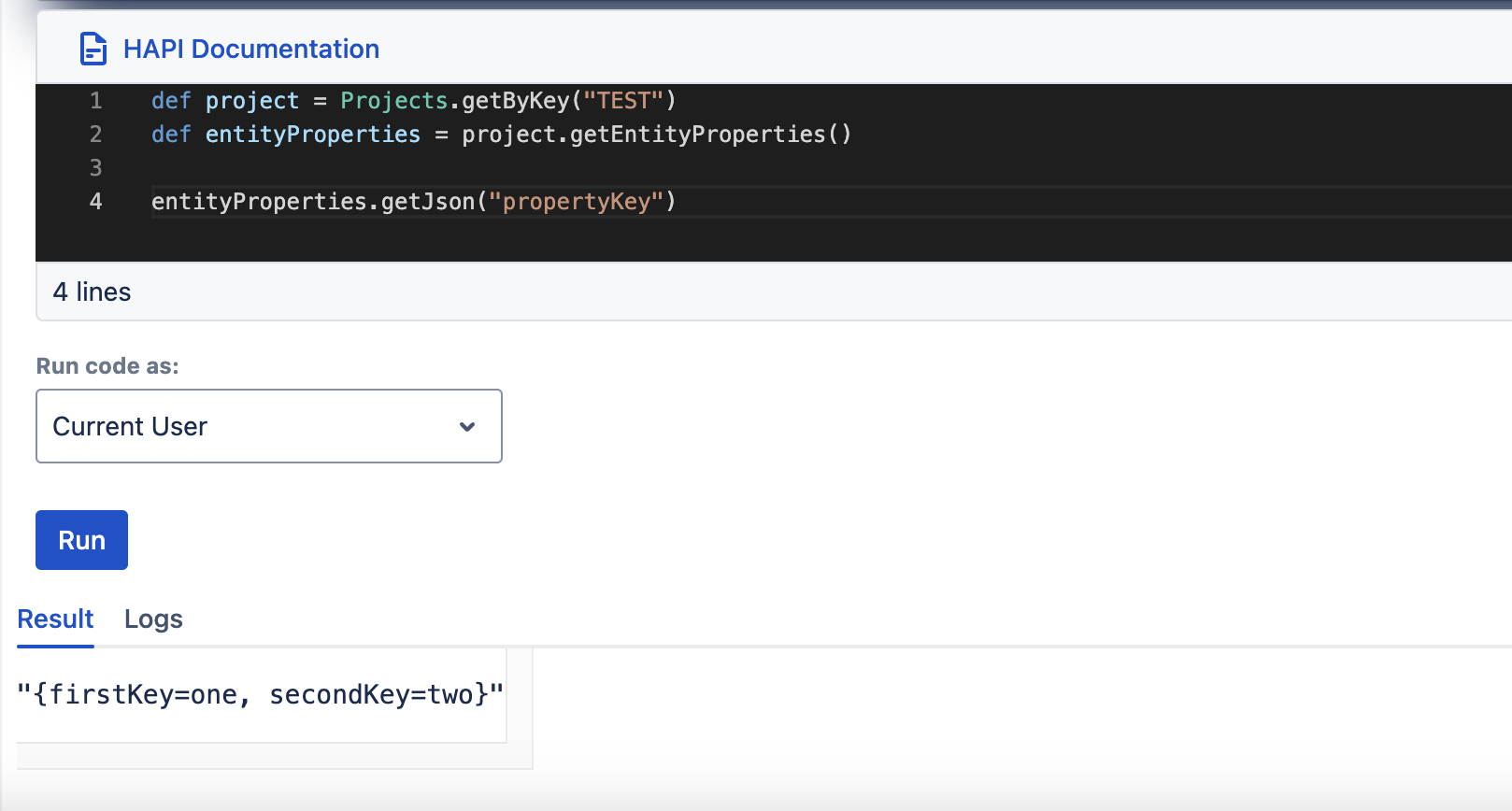
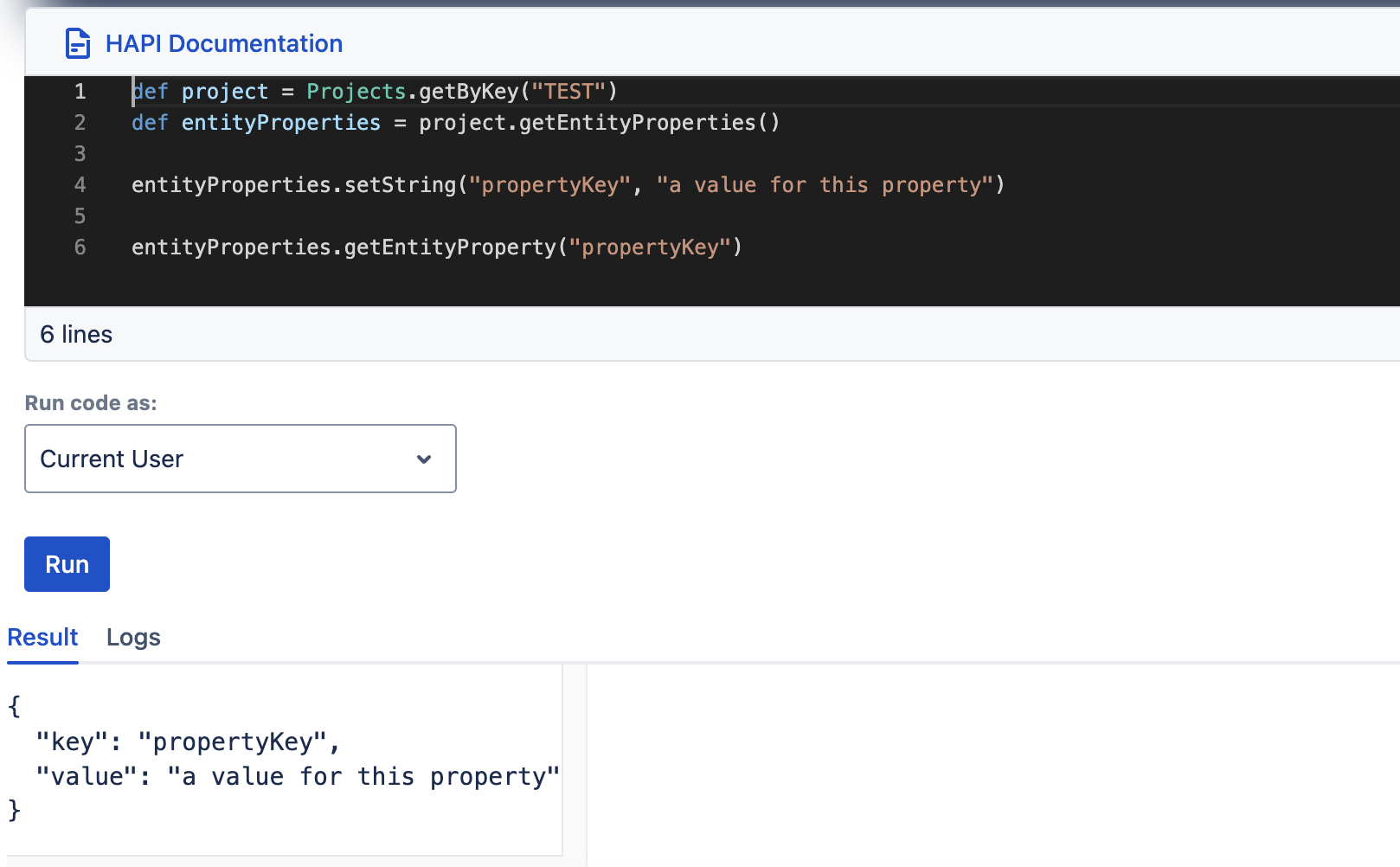
The EntityProperties object can return the full property in the form of an EntityProperty object (singular), which is an original Jira class with two fields: key and value.
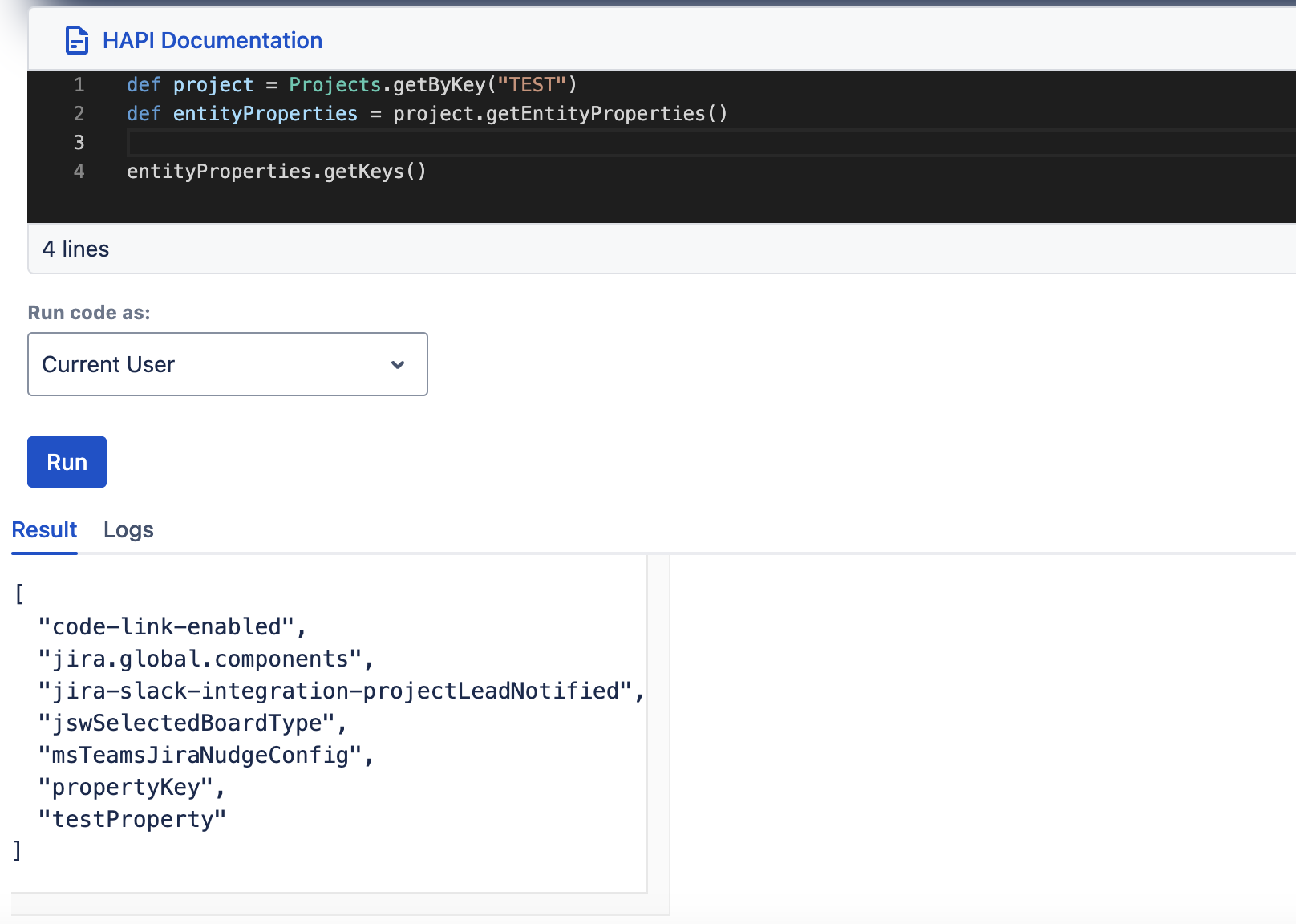
The EntityProperties object owns a method to retrieve a list of all keys of the properties stored against an entity.
The EntityProperties object provides a method to allow you to verify whether a property exist or not:
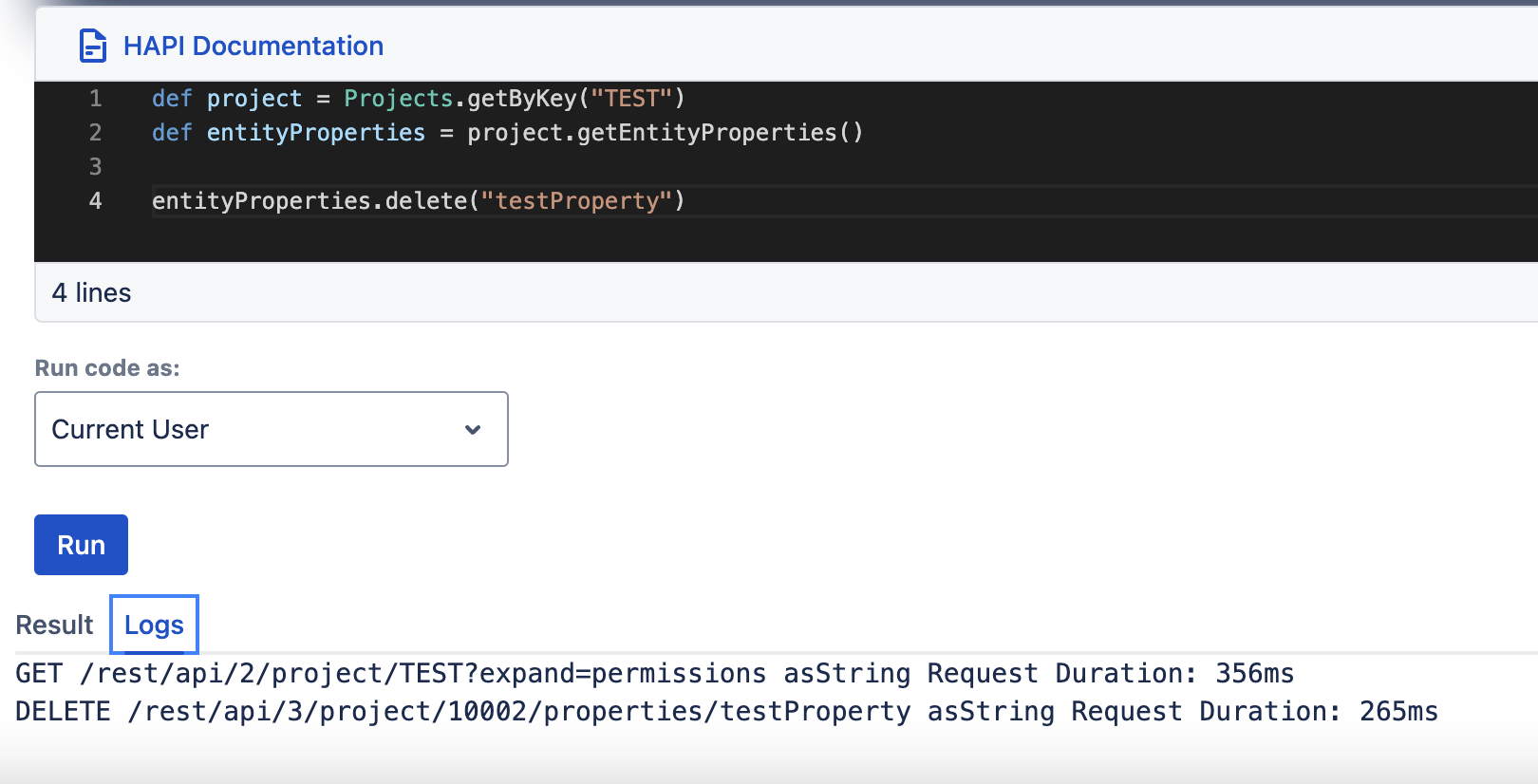
The EntityProperties object provides the functionality to delete a property:
setString, getString
| setString(String key, String value) | getString(String key) |
|---|---|
setInteger, getInteger
| setInteger(String key, Integer integer) | getInteger(String key) |
|---|---|
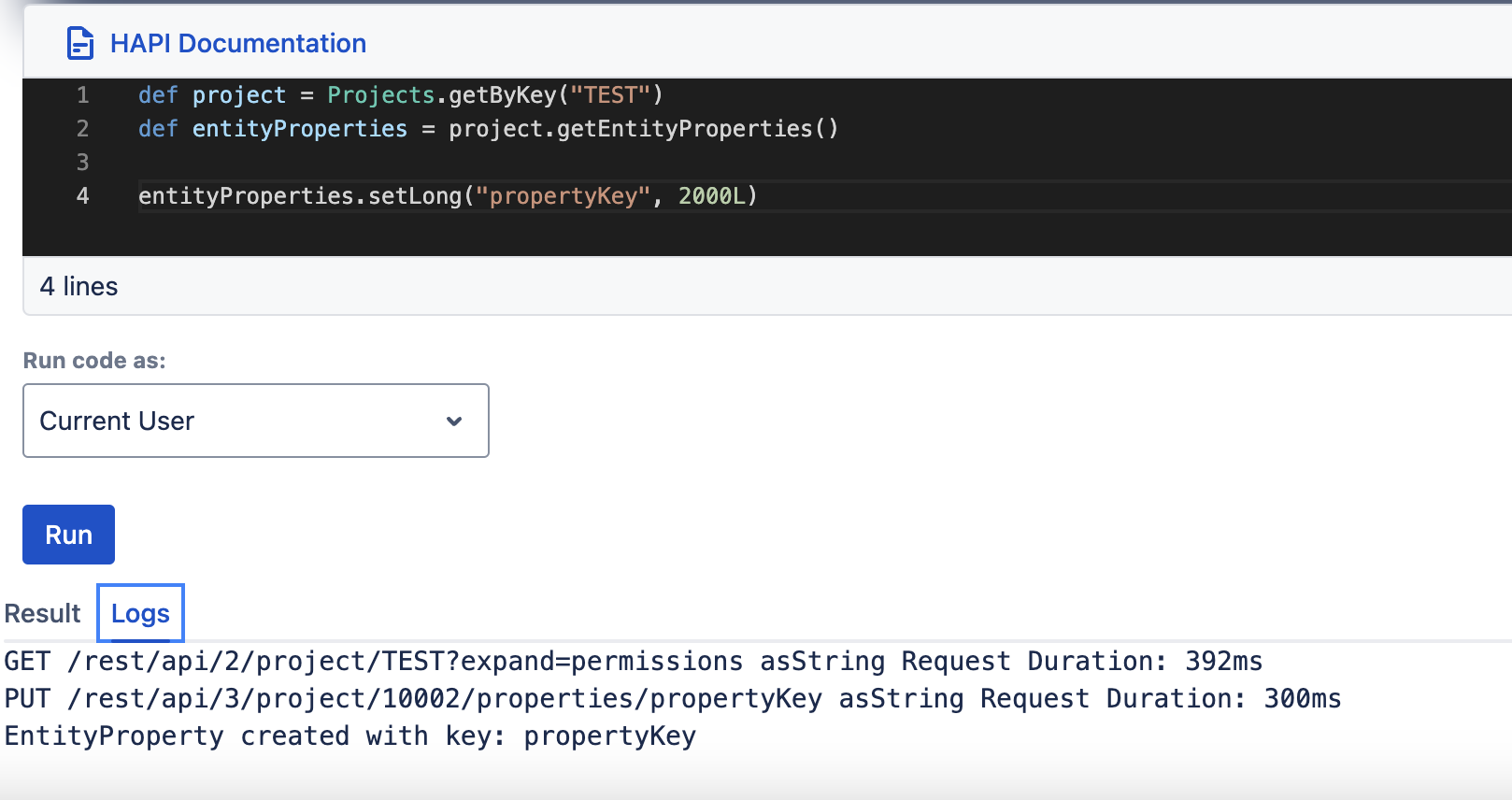
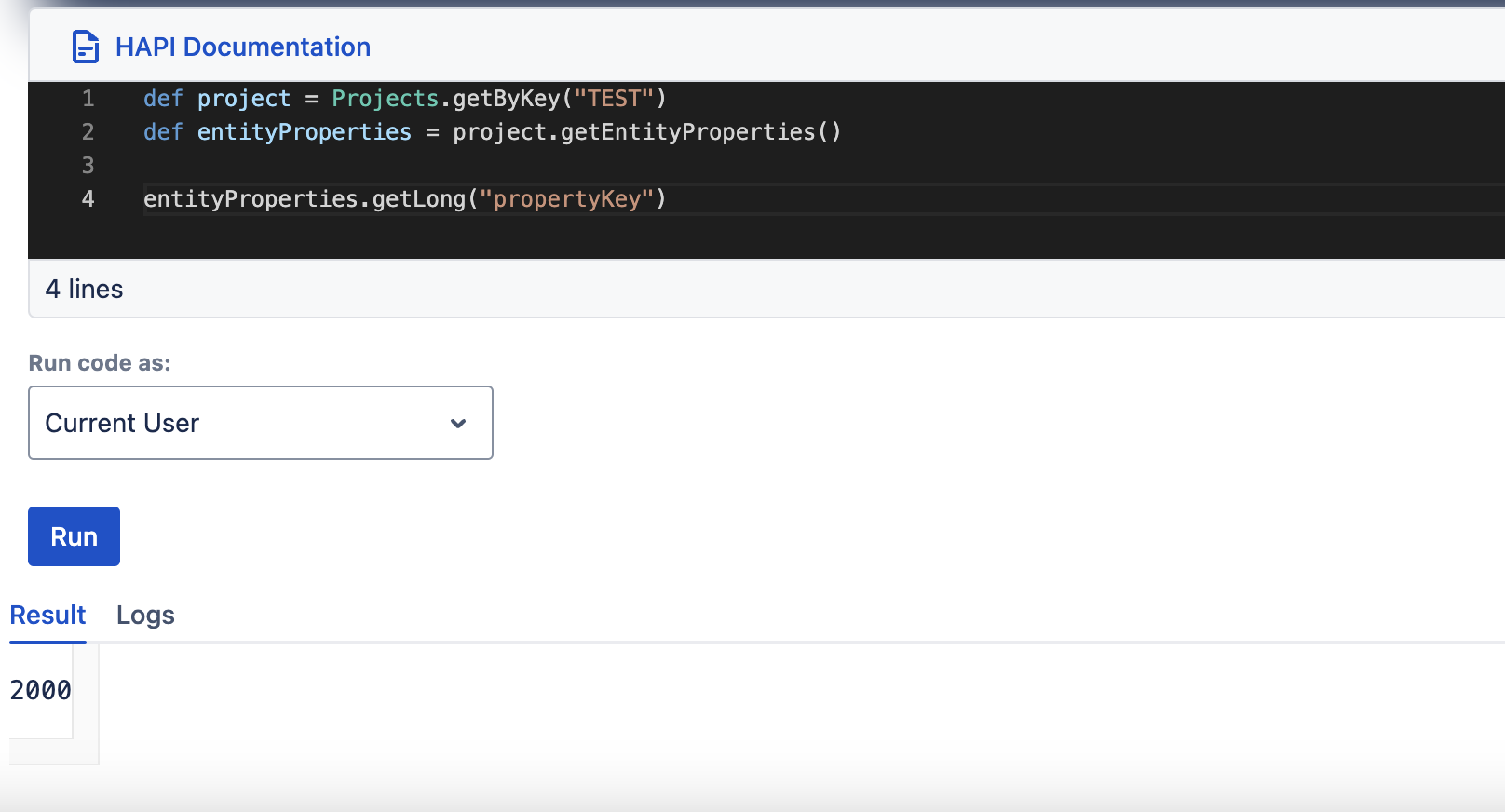
setLong, getLong
| setLong(String key, Long along) | getLong(String key) |
|---|---|
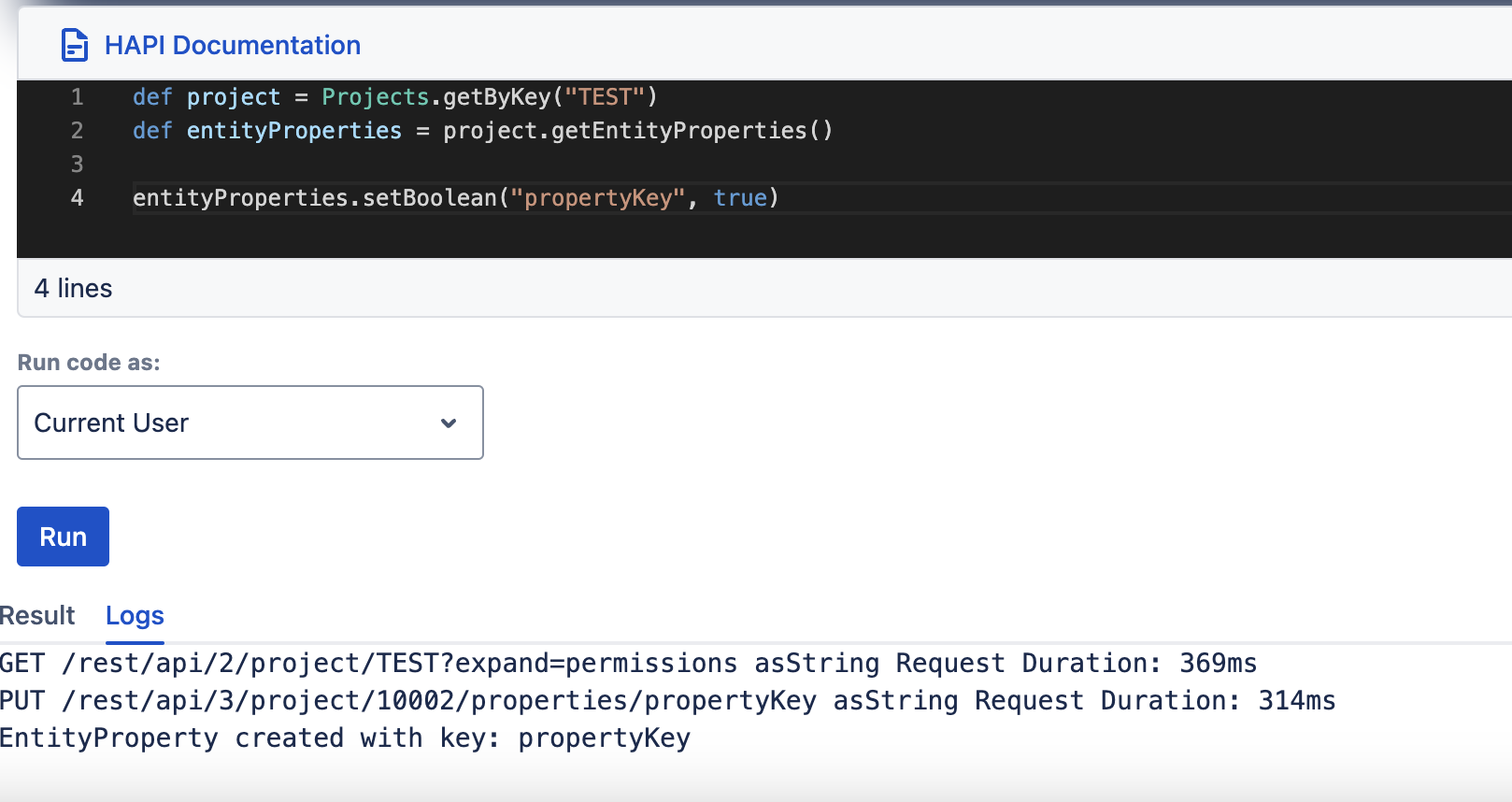
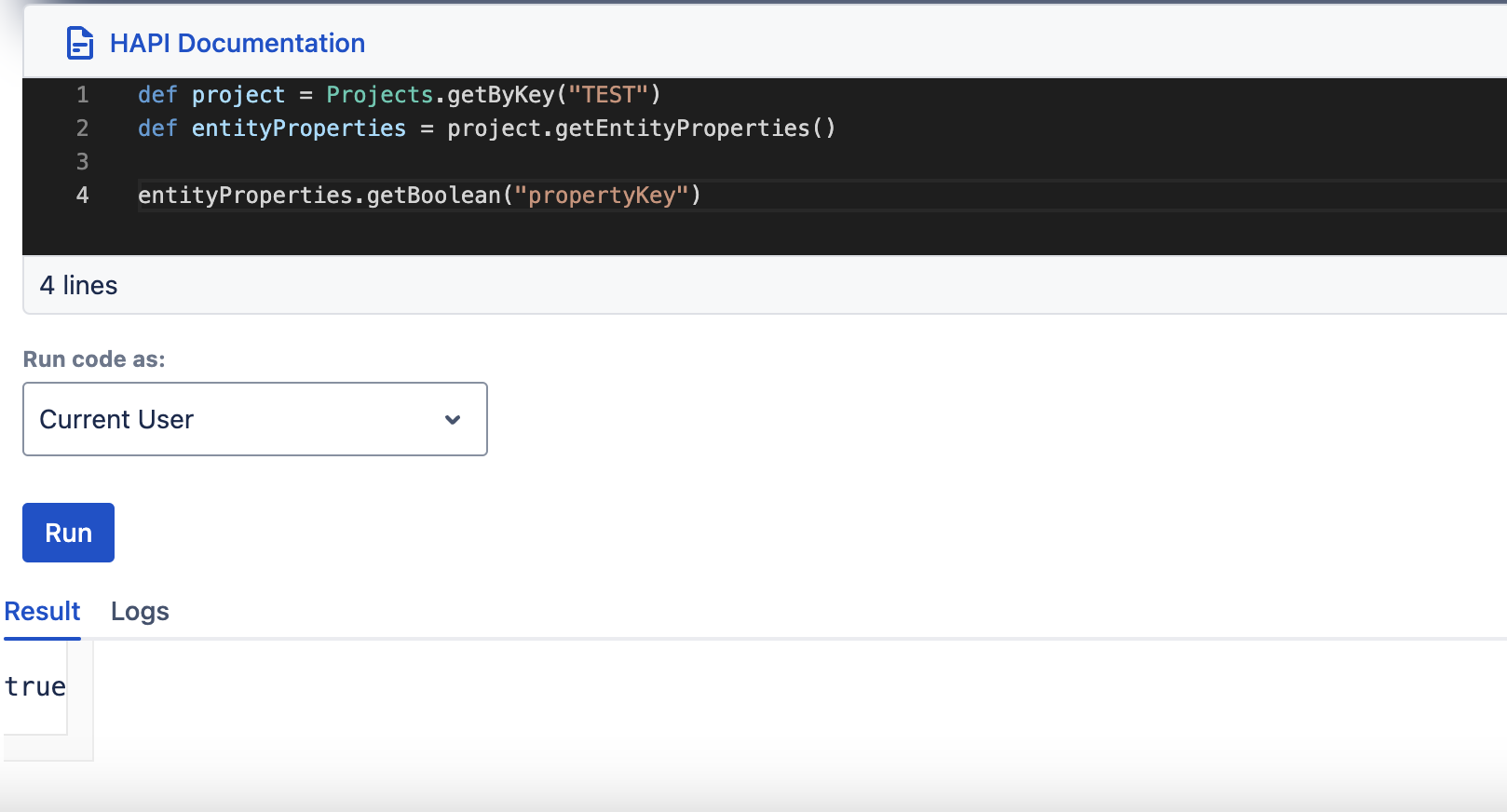
setBoolean, getBoolean
| setBoolean(String key, Boolean bool) | getBoolean(String key) |
|---|---|
setLocalDate, getLocalDate
| setLocalDate(String key, LocalDate date) | getLocalDate(String key) |
|---|---|
setLocalDateTime, getLocalDateTime
| setLocalDateTime(String key, LocalDate dateTime) | getLocalDateTime(String key) |
|---|---|
setJson, getJson
| setJson(String key, String json) | getJson(String key) |
|---|---|
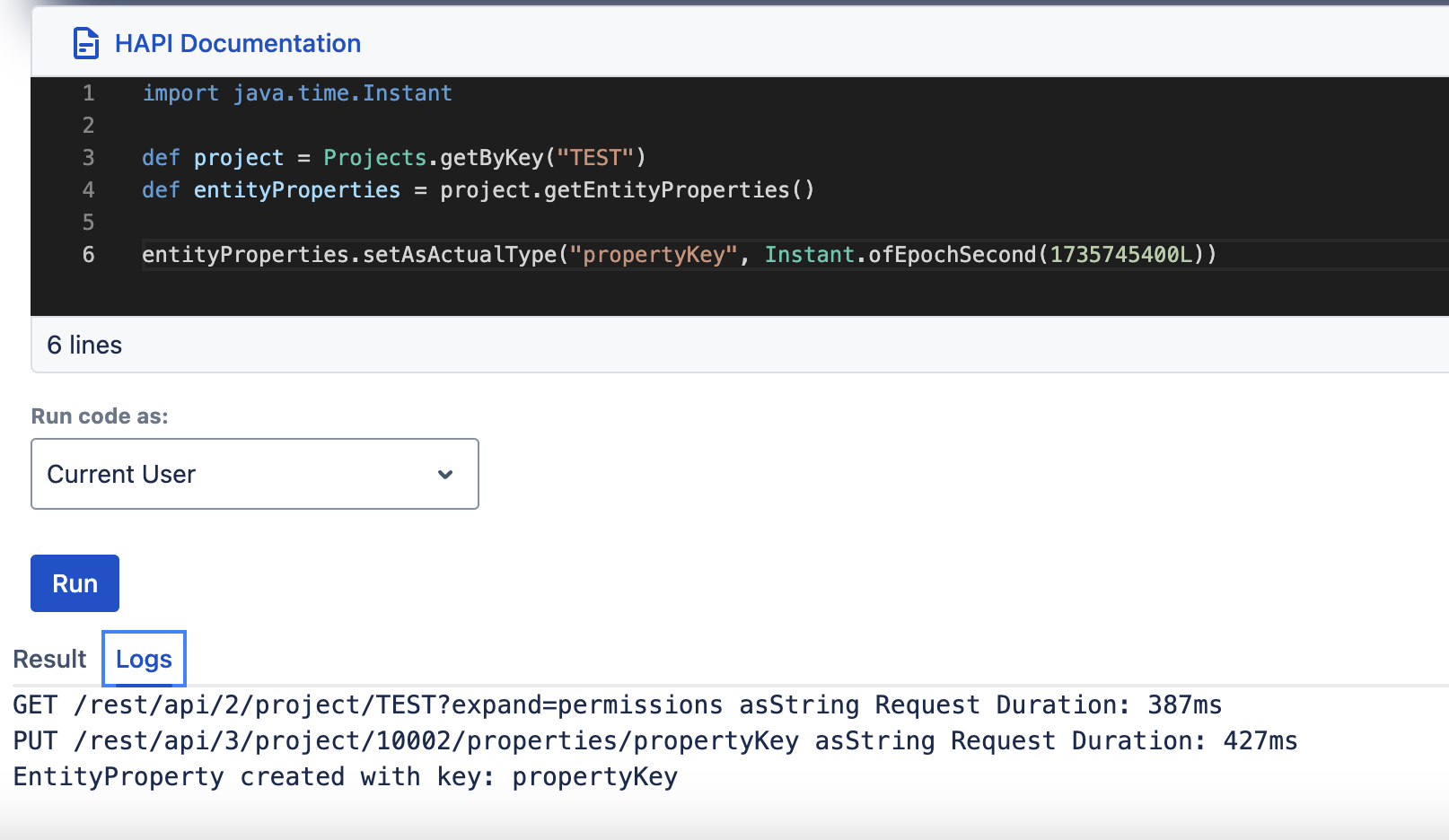
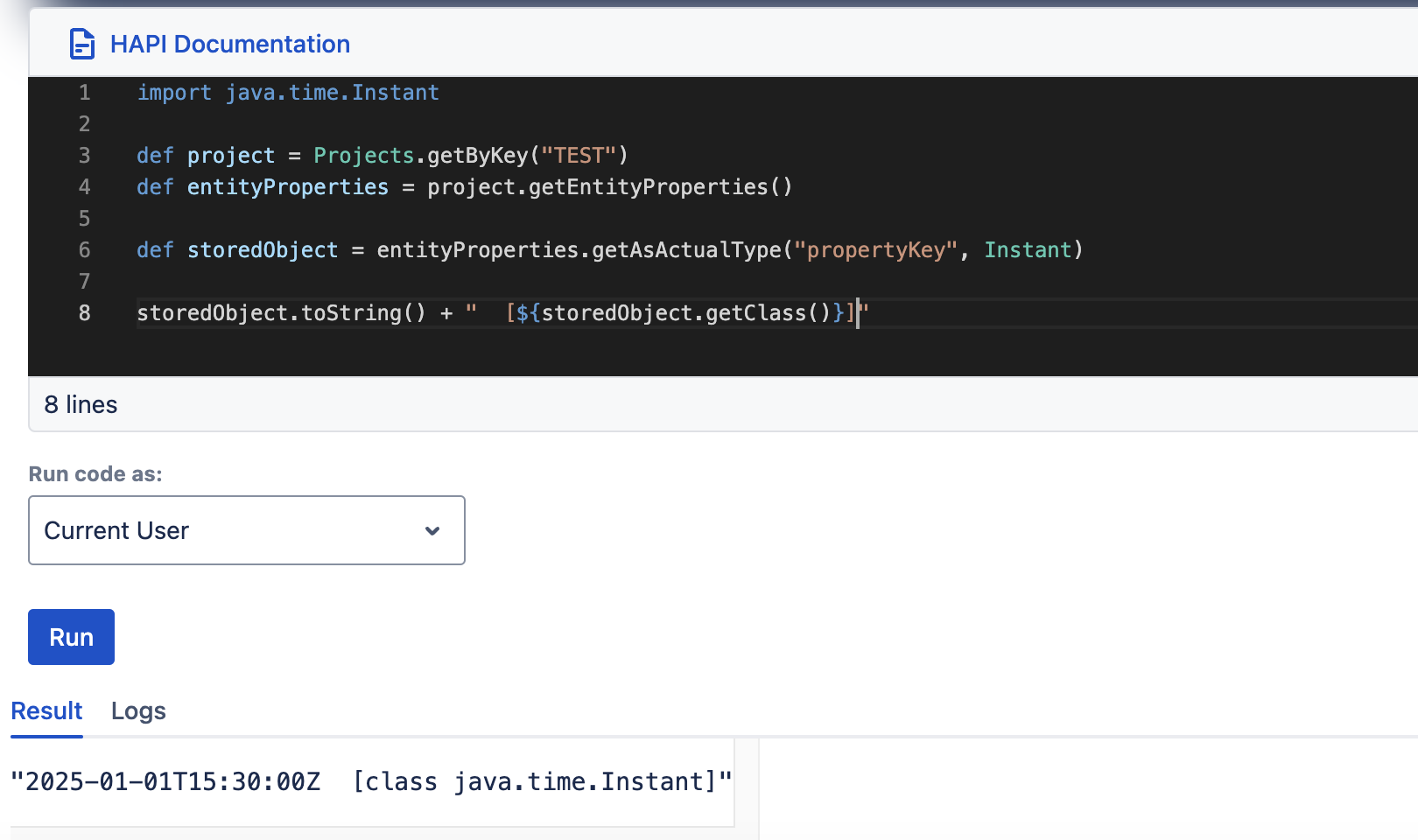
setAsActualType, getAsActualType
| setAsActualType(String key, Object value) | getAsActualType(String key, Class<T> class) |
|---|---|
getEntityProperty
| getEntityProperty(String key) |
|---|
getKeys
| getKeys() |
|---|
propertyExists
| propertyExists(String key) |
|---|
delete
| delete(String key) |
|---|
Related content
- Javadoc for EntityProperties (interface)
- Javadoc for ProjectEntityProperties (Project-specific implementation)
- Javadoc for UserEntityProperties (User-specific implementation)
- Javadoc for IssueEntityProperties (Issue-specific implementation)
- Javadoc for CommentEntityProperties (Comment-specific implementation)