Script Fields in Jira Service Management
Add your ScriptRunner script fields to a Service Management customer portal request form.
Scripted fields are a type of calculated field. Jira Service desk does NOT support these field types. The only exceptions to this are the Database Picker and Issue Picker fields.
Create the required script field. For example, set up a Database Picker field for Affected Server.
Ensure the field is associated with the screen you wish it to appear on:
Navigate to ScriptRunner → Script Fields.
Click the Cog next to the required field, and click Configure Screens.
Check the screens you wish the field to be associated with.
Click Update.
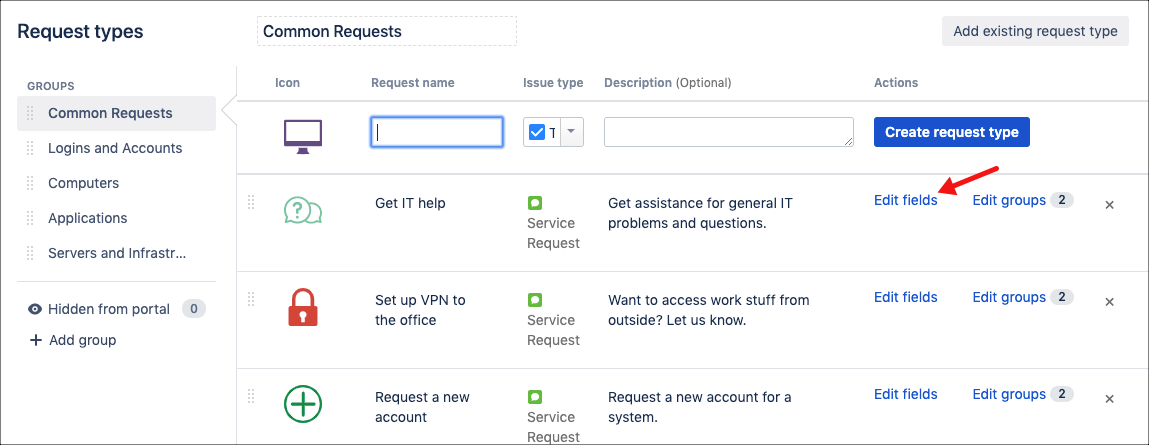
Navigate to your Service Management project and click Project Settings.
Navigate to Request Types in the left menu.
Select Edit fields next to the request type you wish to add the field to.
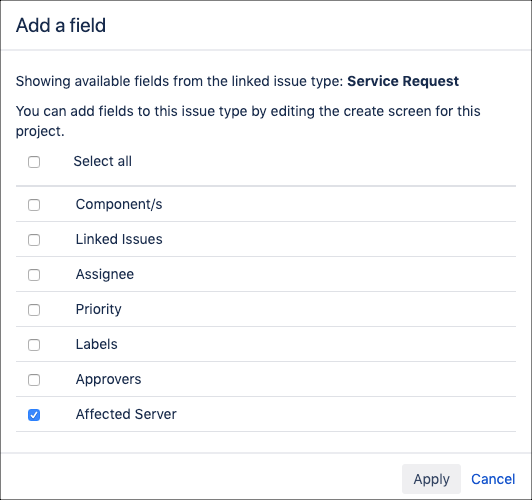
Click Add a Field.
Check your ScriptRunner script field and click Apply.
If your script field does not appear in this list, check you have associated it with the correct screen. You can find the screen your request type uses by going to Project Settings→Screens.
The field is displayed under Hidden Fields with Preset Values. Click Show to make the field visible on the request form.
Scripting Service Management
Currently, in some Service Management versions, behaviours do not work when you click Raise a Request from the project admin screen.
Here are some limited examples for scripting Jira Service Management.
See the documentation about Getting the Most Out of Service Management.
Getting comment visibility levels
Service Management uses entity properties for whether the comment is internal or not, amongst other things.
This is fortunate as it means we don’t need to use the JSD API directly.
From a workflow function
The following code will get the visibility of a comment this transition, and is suitable to be used for the condition field of validators and post-function built-in scripts (such as Sending a Custom Email):
import groovy.json.JsonParserType
import groovy.json.JsonSlurper
def commentProperties = transientVars["commentProperty"] as String[]
def isInternalComment = false
if (commentProperties) {
def commentProperty = commentProperties.first()
def props = new JsonSlurper().setType(JsonParserType.LAX).parseText(commentProperty)
isInternalComment = props.find { it.key == "sd.public.comment" }?.get("value")?.get("internal")
}
isInternalComment.toBoolean()From an event listener
Given an event listener listening for the Issue Commented event, the following code will yield the visibility level of the comment just added:
import com.atlassian.jira.bc.issue.comment.property.CommentPropertyService
import com.atlassian.jira.component.ComponentAccessor
import com.atlassian.jira.issue.comments.Comment
import groovy.json.JsonSlurper
final SD_PUBLIC_COMMENT = "sd.public.comment"
def user = event.getUser()
def comment = event.getComment()
def commentPropertyService = ComponentAccessor.getComponent(CommentPropertyService)
def isInternal = { Comment c ->
def commentProperty = commentPropertyService.getProperty(user, c.id, SD_PUBLIC_COMMENT)
.getEntityProperty().getOrNull()
if (commentProperty) {
def props = new JsonSlurper().parseText(commentProperty.getValue())
(props['internal'] as String).toBoolean()
} else {
null
}
}
if (comment) {
return isInternal(comment)
}
falseReusing this isInternal closure above, you can find all internal/external comments etc:
// Example: find all _external_ comments on issue
log.debug issue.comments.findAll { it.isPublic() }
// iterate comments and check external property
issue.comments.each {
log.debug("Comment on issue ${issue.key}, id: ${it.id}, is public: ${it.isPublic()}")
}Creating internal comments
See Adding comments in Jira Service Management for information on creating internal comments and checking the visibility of comments.